England NHS Timeline
1943
1952

1950s

1969

1970s

1980s
...

1991
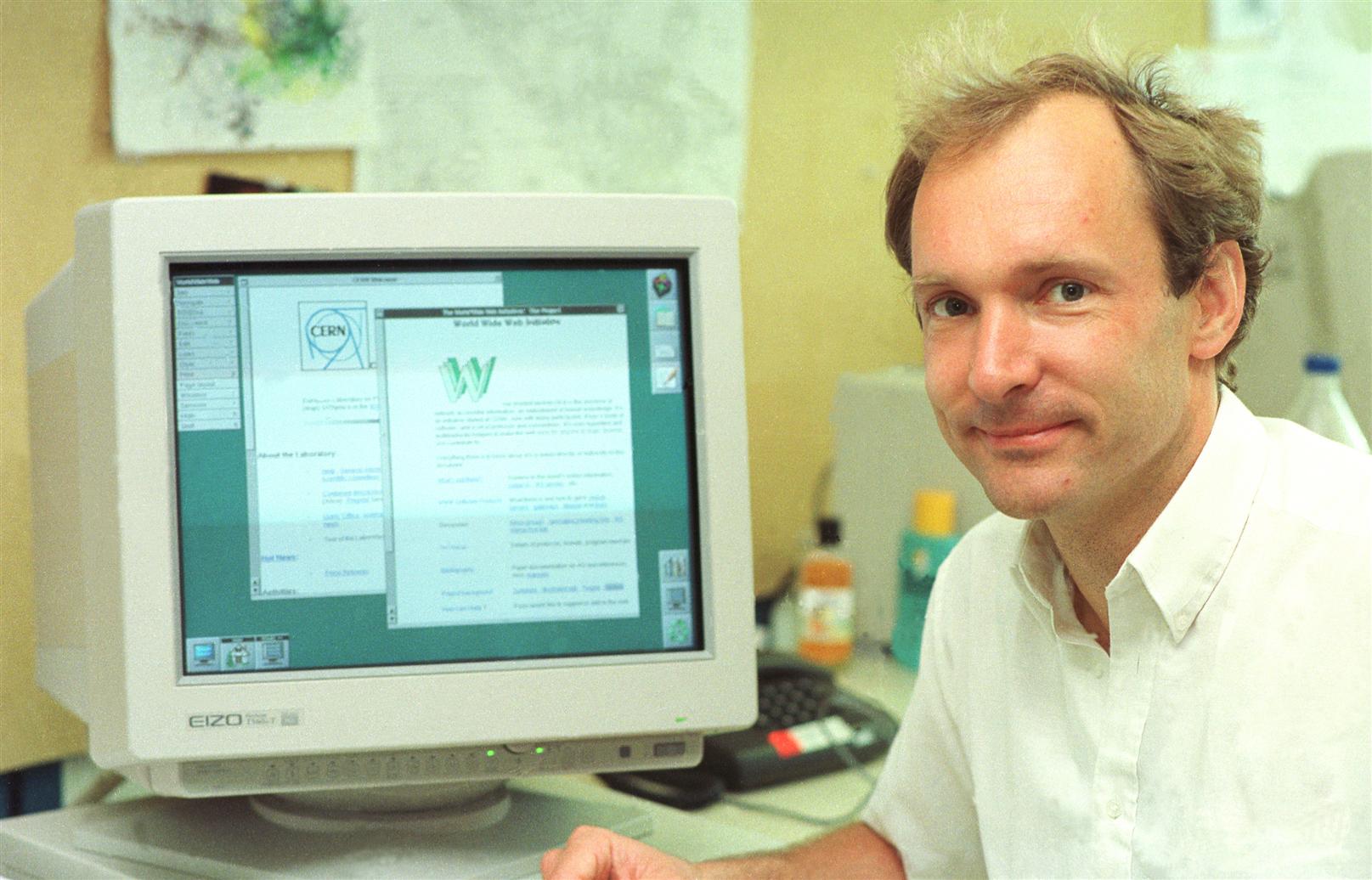

1992

1997

2001

2002

2002-2012
2016

2017

2019

2019

...

...

2020

2022-23

2023

2024
